Ticks are amazingly resilient creatures. They are small arachnids that can cause diseases in humans, pets, livestock, and wildlife. Ticks can live 9 months up to 15 months without food.
Ticks are among the most aggravating and dangerous pests. They transmit many pathogens that cause disease in both humans and other animals. Their bites can cause a variety of allergic reactions.
Table of Contents
How Long Can Ticks Live In Your House?

Ticks can live in your house for up to three months. However, if you’re experiencing symptoms like itching and irritation, or you notice that your pet is acting lethargic or not eating, it’s time to call an exterminator to take care of the problem.
How Long Can Ticks Live in a Car?
Ticks can live in a car for up to 8 weeks. However, they will most likely die if they are not removed from the vehicle. This is because they are cold-blooded animals and cannot regulate their body temperature. Additionally, ticks cannot survive high levels of heat and humidity.
How Long Does It Take a Tick to Starve?
Ticks will begin to starve after 9 months up to 15 months. That’s because ticks have a lot of bacteria living in their gut called Wolbachia, which helps them survive by reducing their need for food.
What Does the Tick Eat?

The tick is a blood-sucking parasite, so they eat and consume the blood of its host. It feeds on the blood of animals, including humans. To be able to feed, ticks must attach to their host. They are generally found in temperate regions, mainly on land and trees. Mice, birds, deer, and other small mammals are common hosts for ticks.
How Much Does a Tick Eat?
A tick can eat anywhere from 2 to 20 times its body weight in blood during a single feeding. The size of the tick determines how much it can consume at one time. You may only see something the size of a sesame seed on your dog’s skin after your dog has been out in the woods for several hours and has been exposed to ticks for some time.
What Do Deer Ticks Eat?
The deer tick, or “deer fly,” is a common insect that can be found in the United States. It’s also known as the dog tick and black-legged tick. The deer fly lives on mammals. However, it prefers to feed on small animals like mice, rabbits, squirrels, and even birds.
The deer tick feeds on blood from its host and then injects its saliva into the wound to help protect itself against predators while it waits for an opportunity to bite again. Deer ticks are attracted to warm and humid areas where they can find hosts, such as deer and other small mammals.
Deer ticks prefer to feed on small rodents. These animals are easier targets than larger mammals such as humans or cattle, which may be harder for a tick to attach itself onto successfully without leaving some kind of mark behind.
Can You Get Lyme Disease From Eating a Tick?
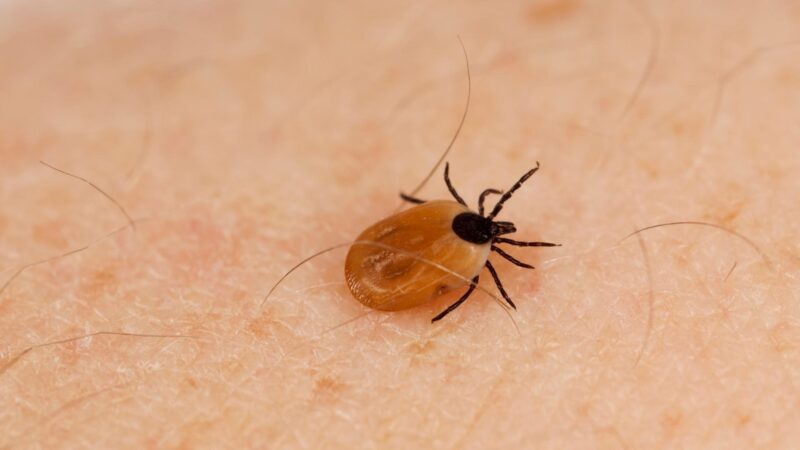
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), eating a tick won’t get you sick. However, it could make your illness worse if you’re already infected with Lyme disease or another type of bacteria.
The most common symptoms of Lyme disease are fever, headache, fatigue, and muscle aches. These symptoms can last for several weeks or months after infection. If left untreated, Lyme disease can cause serious heart problems, arthritis, and neurological problems like memory loss and facial palsy (problems moving facial muscles).
Can Ticks Live In Your Bed?
While not all ticks carry diseases, and the risk of disease transmission from ticks is very low, it’s still important to know that ticks can live on your bed. The parasites are often found in hidden places and have adapted in ways that make them less likely to be noticed by people who don’t check their beds regularly.
Is There a Way to Tell How Long a Tick Has Been Attached?

The only way to know the length of time a tick has been attached is by looking at the amount of blood a tick has taken. The longer a tick has been attached, the more likely it will have sucked up enough blood to become engorged with blood and then detach from its host.
If you can find a tick on your skin and see that it’s attached for several hours, this may be an indication that you’ve been bitten by an infected tick. If this is the case, make sure to use gloves or tweezers while removing the tick from your skin not to spread disease and germs.
Can a Tick Be Dead and Still Attached?
A tick can be dead and still attached. Ticks are arachnids with six legs and two body parts known as “the opisthosoma.” The opisthosoma is the part of the tick that attaches itself to its host. The two body parts are called the prostomium and the metasoma, which, together, make up the entire tick.
The prostomium is where you’ll find your first encounter with a tick. It’s what you see when looking at a live tick. The metasoma is the second body part, which connects to the first by way of an opening called the hypostome. The hypostome has tiny teeth on it that allow it to attach itself to another creature or animal’s skin.
What Are the Odds of Getting Lyme Disease From a Tick?
The likelihood of getting Lyme disease from a tick depends on where you live and what types of ticks are common in your area. The odds of getting Lyme disease from a tick are very low. According to the CDC, out of 300,000 cases of Lyme reported in the US each year, only about 12 people have been found to have been infected with Borrelia burgdorferi, which causes Lyme disease.
Does a Tick Bite Leave a Hard Lump?

A tick bite can leave a hard lump, but it’s not always indicative of disease. In fact, most people don’t even notice a tick bite until they’ve had a few days to develop a rash because they’re usually not as itchy as you might think.
If you have a hard lump on your skin that doesn’t go away within a few days (or if you notice any other symptoms), make sure to get it checked out by your doctor.
Will a Tick Head Eventually Come Out?
Ticks will eventually emerge from the host’s skin. In most cases, the tick head is attached by one of its legs to the host and can be easily removed. However, if the tick head has become firmly attached to a part of your body (for example, your face or hands), it may not be possible to remove it without causing additional damage or infection.
When Should I Worry About a Tick Bite?
It’s important to note that the vast majority of tick bites do not transmit disease. However, if you suffer from an allergy or if you have a weakened immune system due to other medical conditions, you may experience symptoms like itching, swelling, and hives.
If you’ve been bitten by a tick and experience any of these symptoms within two weeks of being bitten by a tick, see a healthcare provider immediately.
Ticks are more than just a nuisance for a lot of people. As you’ve learned in this article, they can carry serious diseases that can alter your life within just days of being bitten.
List of Sources
How Ticks Get Under Your Skin: Insertion Mechanics of the Feeding Apparatus of Ixodes Ricinus Ticks